Intra-embryonic Mesoderm, Foldings of the Embryo, Derivatives of Germ Layers
INTRAEMBRYONIC MESODERM
- Intra-embryonic mesodermal cells are
distributed as a sheet on each side of the median plane.
- A longitudinal groove subdivides the
mesoderm into 3 parts from notochord to periphery of the germ disc-
- Paraxial mesoderm
- Intermediate mesoderm
- Lateral plate mesoderm
PARAXIAL MESODERM
- It is derived from the epiblast cells
migrating through rostral part of primitive streak.
- It extends from the primitive streak to the prochordal
plate.
- It undergoes condensations called somitomeres.
- Caudal to the
otic vesicle somitomeres
further undergo segmentations called somites
or metameres.
- Rostral to the
otic vesicle somitomeres remain
unsegmented.
Count
of Somites –
- The first pair of somites appear on day 20 in the occipital
region.
- Somites continue to appear from 20th to 30th
day in cranio-caudal direction.
- 42 - 44 pairs of somites are formed, which are grouped as –
- Occipital- 4
pairs
- Cervical- 8
pairs
- Thoracic- 12
pairs
- Lumbar- 5
pairs
- Sacral- 5 pairs
- Coccygeal- 8-10
pairs
- Most of the coccygeal pairs disappear and the somites become
reduced to 37 pairs.
Structure of Somites –
- Somite is a triangular mass of mesenchyme.
- Each somite is supplied by a single spinal nerve.
- A small cavity myocele develops in each somite and divides it
into-
- Sclerotome & Dermo-myotome
- Later, myocele obliterates and the somite differentiates into 3
parts-
- Sclerotome- ventromedial part
- Dermatome- dorsolateral part
- Myotome- middle part
INTERMEDIATE MESODERM
- It connects the paraxial mesoderm with lateral
plate mesoderm.
- It projects into the dorsal wall of coelomic cavity
on each side of dorsal mesentery of gut.
- It shows segmentations in the cervical and upper
thoracic regions.
- Caudally it forms unsegmented column of cells known as nephrogenic cord.
LATERAL PLATE MESODERM
- It is derived from the middle of primitive
streak.
- It is unsegmented.
- Peripherally it is continuous with
extra-embryonic mesoderm.
- Cephalic to the buccopharyngeal membrane it is
continuous with pericardial bar.
- During the somite period a series of clefts
appear within the lateral plate.
- The clefts coalesce with one another to form intra-embryonic
coelom.
- The coelomic cavity divides the lateral plate into 2 layers-
- Somatopleuric layer
- Splanchnopleuric layer
- Later, intra-embryonic
coelom communicates with extra-embryonic coelom at the periphery of embryonic
disc, except in the cephalic part, where it is continuous with pericardial
bar.
- In the cephalic part lateral plate mesoderm forms horse-shoe shaped area adjoining the pericardial sac known as septum transversum.
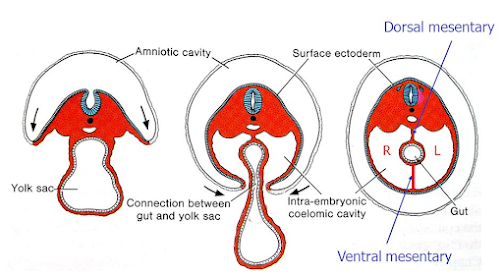
FOLDINGS OF THE EMBRYO
- At the end of 3rd week embryonic
area shows development of head fold, tail fold and two
lateral folds.
- Foldings convert the flattened germ disc
into cylindrical embryo.
- During the process of embryonic folds, the
growth of yolk sac is reduced and amniotic cavity enlarges, so that
the embryo floats in the amniotic fluid.
- Foldings converge on
the ventral surface of embryo and form primitive umbilical ring.
- Amniotic membrane forms a tubular
investment around the connecting stalk at the umbilical ring and
converts it into umbilical cord.
- The yolk sac cavity
within the embryonic folds forms primitive gut.
- The extra-embryonic
part of yolk sac cavity forms umbilical vesicle, which is connected
to the primitive gut by vitello-intestinal duct.
Head Fold
:-
- Head fold is mainly caused by the rapid and longitudinal growth of central nervous system.
The
germ disc bends ventrally towards the yolk sac around the cranial end of
notochord
So that the fore brain vesicle occupies the cephalic end of embryo
- The part of yolk sac contained within the
head fold is known as fore gut.
- Dorsal wall of the fore gut is supported by notochord and hind
brain vesicle of neural tube.
- Ventral wall of the fore gut presents buccopharyngeal membrane, pericardial
sac with primitive heart tube and septum transversum.
- Buccopharyngeal membrane
lies at the bottom of a depression on the surface ectoderm known as stomodeum.
- Buccopharyngeal membrane
ruptures during the 4th week, so that the fore gut communicates
with stomodeum and amniotic fluid gains entrance into the gut.
- Tail fold is mainly caused by the rapid and longitudinal growth of central nervous system.
The germ disc bends ventrally towards the yolk sac around the caudal end of notochord
So that the caudal end of neural tube surrounds the caudal end of embryo
- The part of yolk sac contained within the tail
fold is known as hind gut.
- Dorsal wall of the fore gut is supported by notochord, neural
tube, primitive node and primitive streak.
- Ventral wall of the hind gut presents connecting stalk with allanto-enteric
diverticulum and cloacal membrane.
- Cloacal membrane lies at the bottom of a
depression on the surface ectoderm known as ectodermal cloaca.
Lateral
Folds :-
- Lateral folds are mainly caused by the formation of rapidly growing somites.
The lateral margins of germ disc bend ventrally towards the yolk sac and form lateral folds
Somatopleuric
and splanchnopleuric layers of lateral plate mesoderm in each lateral
fold, fuse with the corresponding layers ventrally, except at the umbilical ring.
Now the continuous somatopleuric layer lines the parietal body wall
Splanchnopleuric layers invest primitive gut and reflect dorsally as dorsal mesentery, ventrally as ventral mesentery
Thus, the intra-embryonic coelomic cavity is well defined between the somatopleuric and splanchnopleuric layers
- The part of yolk sac contained within the lateral
folds is known as mid gut.
- Mid gut is connected to the umbilical vesicle by vitello-intestinal duct through primitive umbilical ring.
DERIVATIVES OF GERM LAYERS
DERIVATIVES
OF ECTODERM
- Derivatives of
Surface Ectoderm
- Derivatives of
Neural Tube
- Derivatives of
Neural Crest Cells
Derivatives of Surface
Ectoderm :-
- Epidermis, hair and nail
- Sebaceous glands and sweat glands
- Olfactory pit
- Optic vesicle and lens vesicle
- Otic vesicle
- Branchial clefts
- Rathke’s pouch, Pituitary glands
- Epithelial lining of cheek, gum, teeth enamel, floor of mouth, nasal cavity and paranasal air sinuses
- Salivary glands
- Mammary glands
Derivatives of Neural
Tube :-
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Neurohypophysis of pituitary gland
- Motor neurons
- Retina
Derivatives of Neural
Crest
Cells :-
Neuronal
Cells –
- Sensory ganglia of cranial nerves V, VII, IX, X
- Spinal ganglia
- Ganglion cells of the autonomic nervous system
Supportive
Cells of the Nervous System –
- Glial cells of the peripheral ganglia
- Schwann cells of peripheral nerves
- Meninges of the forebrain
Pigment Cells
– (except for pigmented retina)
Endocrine
and Para-endocrine Cells –
- Adrenomedullary cells
- Calcitonin-producing cells
- Type I cells of the carotid body
Mesectodermal
Derivatives –
- Visceral and facial skeleton
- Cranial vault
- Walls of large arteries derived from the aortic arches
- Connective tissue of thymus and parathyroid glands
- Dermis of neck and facial regions
DERIVATIVES
OF MESODERM
- Derivatives of Paraxial
Mesoderm / Somites
- Derivatives of Intermediate
Mesoderm
- Derivatives of Lateral
Plate Mesoderm
Derivatives of Paraxial Mesoderm / Somites :-
- Pre-otic somitomeres form striated muscles of Head, extrinsic muscles of the eye, base of skull, calvaria.
- Occipital somites form muscles of the tongue
- Sclerotome forms ribs and vertebrae
- Myotome forms skeletal muscles
- Dermatome forms dermis of the skin
Derivatives of Intermediate
Mesoderm :-
- Genital & Urinary systems
Derivatives of Lateral
Plate Mesoderm :-
Somatopleuric
Layer Derivatives –
- Parietal layers of peritoneal, pericardial and pleural cavities.
- Dermis of skin
- Pectoral and pelvic girdles
- Skeletal elements of limbs
Splanchnopleuric
Layer Derivatives –
- Visceral layer of pericardial, peritoneal and pleural cavities.
- Musculature and connective tissue of gut, respiratory tract and heart.
DERIVATIVES
OF ENDODERM
- Derivatives of Foregut
- Derivatives of Midgut
- Derivatives of Hindgut
Derivatives of Foregut
:-
- Lining of epithelium
of tongue, floor of mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, duodenum up to
the ampulla of Vater.
- Lining epithelium of respiratory
system, auditory tube, tympanic cavity.
- Parenchyma of tonsil,
thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, liver and pancreas.
Derivatives of Midgut
:-
- Lining epithelium of distal
part of duodenum, jejunum, ileum, caecum, appendix, ascending colon, right
2/3rd of transverse colon.
Derivatives of Hindgut
:-
- Lining epithelium of left
1/3rd of transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon,
rectum, anal canal up to mucocutaneous junction.
- Lining epithelium of urinary
bladder, urethra, vagina.
- Parenchyma of prostate, bulbourethral gland.