Posterior Triangle of Neck
POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK
(Find the Video Tutorial Here
👇
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-nJQWzkv1Gc)
- The side of the neck is divided diagonally by sternocleidomastoid muscle into anterior & posterior triangles.
- Posterior triangle of the neck lies behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
BOUNDARIES
In Front :-
- Posterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Behind :-
- Anterior border of trapezius muscle.
Apex :-
- Superior nuchal line of the occipital bone.
Base :-
- Middle 1/3rd of the clavicle.
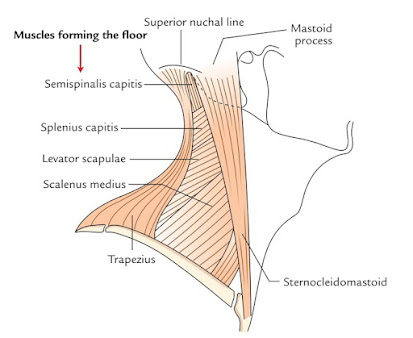
Floor :-
- Semispinalis capitis (occasional)
- Splenius capitis
- Levator scapulae
- Scalenus posterior
- Scalenus medius
- Outer border of first rib
- First digitation of Serratus anterior
- Prevertebral fascia covering all the floor structures
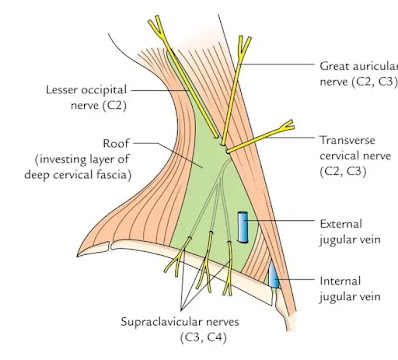
Roof :-
- Skin, superficial fascia, platysma, investing layer of deep cervical fascia.
- The roof is crossed by supraclavicular nerves & external jugular vein.
SUBDIVISIONS
- 2.5cm above the clavicle inferior belly of omohyoid muscle divides the triangle into-
- Upper large Occipital triangle &
- Lower small Supra-clavicular / Subclavian triangle
Occipital Triangle :-
Boundaries –
In front- Posterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Behind- Anterior border of trapezius muscle.
Apex- Superior nuchal line of the occipital bone.
Base- Inferior belly of omohyoid muscle.
Floor- Semispinalis capitis (occasional), splenius capitis, levator scapulae, scalenus posterior, scalenus medius, prevertebral fascia covering the floor structures.
Roof- Skin, superficial fascia, platysma, investing layer of deep cervical fascia pierced by lesser occipital, great auricular, transverse cervical nerves.
Supraclavicular / Subclavian Triangle
:-
Boundaries –
In front- Posterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Behind- Inferior belly of omohyoid muscle.
Apex- Meeting point of sternocleidomastoid & Inferior belly of omohyoid muscles.
Base- Middle 1/3rd of the clavicle.
Floor- Outer border of first rib, first digitation of serratus anterior, prevertebral fascia covering the floor structures.
Roof- Skin, superficial fascia, platysma, investing layer of deep cervical fascia pierced by supraclavicular nerves & external jugular vein, omohyoid fascia.
CONTENTS
In Occipital Triangle :-
Nerves –
- Spinal part of Accessory nerve
- 3rd & 4th Cervical nerves
- Dorsal scapular nerve
- 4 Cutaneous branches of cervical plexus
Arteries –
- Occipital artery
- Superficial cervical artery
In Supraclavicular / Subclavian
Triangle :-
Nerves –
- Trunks of Brachial plexus
- Suprascapular nerve
- Nerve to Subclavius
- Long thoracic nerve
Arteries –
- Third part of Subclavian artery
- Superficial cervical artery
- Suprascapular artery
- Dorsal scapular artery
Lymph nodes –
- Supraclavicular lymph nodes
CONTENTS DESCRIPTION
Nerves :-
Spinal part of Accessory nerve –
It appears in the
triangle deep to the mid-point of posterior border of sternocleidomastoid
here it is hooked
by lesser occipital nerve
surrounded by group of superficial cervical lymph nodes
then it passes downward and backward resting on the levator scapulae
it disappears under cover of anterior border of trapezius.
- It is the only genuine content of the triangle passing between the fascial roof and floor.
- It provides motor supply to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
- It divides the posterior triangle into a care free zone above and care full zone below, as most of the structures lie below the nerve.
3rd & 4th Cervical nerves –
They convey muscular branches from cervical plexus
pass below & parallel with accessory nerve deep to prevertebral fascia
provide branches to
levator scapulae and trapezius
Dorsal scapular nerve –
It conveys fibres from C5 root of the brachial plexus
it enters the triangle by piercing scalenus medius muscle
then it passes backward and downward under cover of prevertebral fascia
it disappears
beneath the levator scapulae to supply rhomboids.
4 Cutaneous branches of Cervical plexus –
They pierce fascial floor pass for a short distance trough posterior triangle
they radiate from middle of posterior border of sternocleidomastoid
within the triangle
then they pierce
the fascial roof and become cutaneous.
Lesser occipital nerve (C2)-
- It runs upward along the posterior border of sternomastoid muscle.
Great auricular nerve (C2 C3)-
- It ascends obliquely across the sternomastoid muscle along the external jugular vein.
Transverse cervical nerve (C2 C3)-
- It runs forward across the sternomastoid muscle towards anterior triangle.
Supraclavicular nerve (C3 C4)-
- It descends beneath the platysma.
- It divides into medial, intermediate, lateral branches which pierce the deep fascia above the clavicle.
- Intermediate branch occasionally pierces the clavicle.
Trunks of Brachial plexus –
- They emerge between the scalenus anterior and medius muscles.
- They lie beneath the prevertebral fascia.
- Upper and middle trunks are situated above & lower trunk behind the third part of subclavian artery.
- Closer to the clavicle each trunk splits into anterior and posterior divisions.
Suprascapular nerve –
- It is a branch of upper trunk.
- It conveys fibres from C5 C6.
- It passes laterally deep to inferior belly of omohyoid and trapezius.
Nerve to Subclavius –
- Tit arises from upper trunk carrying C5 C6 fibres.
- It passes downward in front of brachial plexus and subclavian vessels.
Long thoracic nerve –
- It arises from C5 C6 C7 roots of brachial plexus.
- It runs downward behind the brachial plexus and third part of subclavian artery.
Arteries :-
Occipital artery –
- It is a branch of external carotid artery.
- It appears at the apex of occipital triangle.
- It rests on semispinalis capitis muscle.
Third part of Subclavian artery –
- It appears in the subclavian triangle between the scalenus anterior and scalenus medius.
- It runs downward and laterally resting in a groove on the upper surface of first rib.
- It gives a branch in the triangle called dorsal scapular artery.
Superficial cervical artery –
- It is a branch of thyrocervical trunk from first part of subclavian artery.
- It passes upward and laterally in front of brachial plexus.
- It disappears deep to trapezius muscle.
Suprascapular artery –
- It is a branch of thyrocervical trunk from first part of subclavian artery.
- It passes downward laterally in front of subclavian artery and brachial plexus.
- It runs behind and parallel to the clavicle.
- It leaves the triangle by passing deep to the inferior belly of omohyoid.
Dorsal scapular artery –
- It is a branch of third part of subclavian artery.
- It passes laterally in front of scalenus medius and through the brachial plexus.
- It accompanies dorsal scapular nerve and leaves the triangle deep to levator scapulae.
Lymph Nodes –
Supraclavicular lymph nodes –
- They are situated along the inferior belly of omohyoid between fascial roof and floor.
- They lie superficial to brachial plexus and subclavian vessels.
APPLIED ASPECTS
Virchow’s Nodes :-
- Enlarged left supraclavicular lymph nodes.
- Found in the malignant growth of stomach, testis etc.
Accessory Phrenic Nerve :-
- Sometimes, nerve to subclavius gives a twig from C5 to join the phrenic nerve.
- Such branch loops around the subclavian vein before it joins the phrenic nerve.
- In surgical operations of phrenic avulsion, accessory phrenic nerve might tear the subclavian vein.