Femoral Triangle
FEMORAL TRIANGLE
LOCATION :-
- It is a triangular depression on the upper 1/3rd of front of thigh, below the inguinal ligament.
BOUNDARIES :-
Laterally :- Medial border of sartorius
Medially :- Medial border of adductor longus
Floor :- Gutter-shaped, formed from lateral to medial side by-
- Iliacus, tendon of psoas major, pectineus & adductor longus muscles.
Roof :- Skin, superficial fascia with superficial inguinal lymph nodes & great saphenous vein, fascia lata with saphenous opening.
Base :- Inguinal ligament
Apex :- Meeting point of sartorius & adductor longus muscles.
CONTENTS :-
- Femoral Vein
- Femoral Artery
- Femoral Sheath
- Deep Inguinal Lymph Node
- Femoral Nerve
- Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
- Femoral Branch of Genito-femoral Nerve
- Fibro-fatty Tissue
FEMORAL VEIN :-
- It is a deep vein, provided with valves.
- It enters the triangle through the apex, where it lies behind the femoral artery.
- Ascends along the medial side of the artery, towards the inguinal ligament.
- Deep to the ligament it continues as external iliac vein.
Tributaries in the Triangle :-
- Profunda femoris vein
- Great saphenous vein
FEMORAL ARTERY :-
- It is the continuation of external iliac artery
- It enters the triangle behind the inguinal ligament at mid-inguinal point.
- It leaves the triangle through the apex.
- Proximal 3-4cm of the artery along with femoral vein are enclosed in femoral sheath.
Relations in the Triangle :-
In front -
- In the upper part- Skin, superficial fascia, superficial inguinal lymph nodes, fascia lata, femoral sheath, femoral branch of genito-femoral nerve.
- In the lower part- Medial femoral cutaneous nerve
Behind -
- In the upper part- Femoral sheath, psoas tendon, pectineus, hip joint.
- In the lower part- Adductor longus, femoral vein.
Medially - Femoral vein
Laterally -
- In the upper part- Femoral nerve
- In the lower part- Medial femoral cutaneous nerve, saphenous nerve.
Branches in the Triangle :-
Superficial epigastric artery -
- Pierces the femoral sheath & cribriform fascia.
- Runs upwards & supplies the skin over the umbilical region.
Superficial circumflex iliac artery -
- Pierces the femoral sheath & fascia lata.
- Runs laterally towards anterior superior iliac spine & participates in spinous anastomosis.
Superficial external pudendal artery -
- Pierces the femoral sheath & cribriform fascia.
- Runs medially in front of the spermatic cord / round ligament of uterus.
- Supplies the skin over the scrotum / labium majus.
Deep external pudendal artery -
- Pierces the femoral sheath & fascia lata.
- Runs medially deep to the spermatic cord / round ligament of uterus.
- Supplies the scrotum / labium majus.
Muscular branches - Supply the muscles of triangle.
Profunda femoris artery -
It is the largest branch of femoral artery.
Arises from the lateral side of femoral artery 3.5cm below the inguinal ligament.
It spirals behind the femoral vessels.
It leaves the triangle by passing between pectineus & adductor longus muscles.
Branches of Profunda femoris in the femoral triangle -
Lateral circumflex femoral artery-
- Passes laterally between the anterior & posterior divisions of femoral nerve.
- Divides into- Ascending, transverse & descending branches.
- Ascending branch takes part in spinous anastomosis.
- Transverse branch takes part in cruciate anastomosis.
- Descending branch takes part in genicular anastomosis.
Medial circumflex femoral artery-
- It runs behind the femoral artery.
- Leaves the triangle by passing between psoas & pectineus muscles.
FEMORAL SHEATH :-
- It is a funnel-shaped fascial prolongation around the proximal 3-4cm of femoral blood vessels.
Formation :-
- It is derived from extra-peritoneal connective tissue.
- It has 4 walls..
- Anterior wall- Formed by fascia transversalis.
- Posterior wall- Formed by fascia iliaca.
- Lateral wall- Vertical
- Medial wall- Slopes downward & laterally.
Function :-
- It allows the femoral vessels to glide freely during the movements of hip joint.
Relations :-
- Femoral nerve lies outside (lateral to) the sheath.
- Saphenous opening lies in front of the sheath.
- Cribriform fascia covers only the antero-medial surface of the sheath.
Subdivisions :-
- 2 antero-posterior septa divide the sheath into 3 compartments.
- Lateral, intermediate & medial compartments.
Intermediate compartment - contains femoral vein.
Medial compartment (Femoral canal) -
- It is conical, 1.25cm long.
- It is a dead space, contains a deep inguinal lymph node (of Cloquet / Rosenmuller).
- It allows the expansion of femoral vein during increased venous return.
- Its base is directed above & surrounded by oval shaped femoral ring.
- Femoral ring-
- It is wider in females.
- It is bounded by..
- Inguinal ligament-anteriorly
- Pectineus muscle with its fascia-posteriorly
- Lacunar ligament-medially
- Femoral vein-laterally
- It is closed by femoral septum.
- A depression lies above the femoral septum, known as femoral fossa.
Structures Piercing the Sheath :-
- Laterally- Femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve.
- In front- Superficial epigastric, superficial circumflex iliac & superficial external pudendal branches of femoral artery.
- Medially- Great saphenous vein.
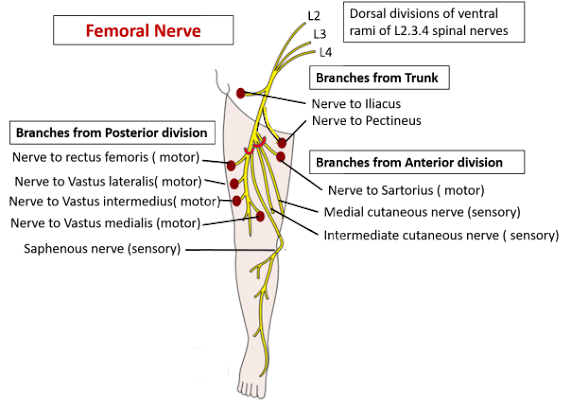
FEMORAL NERVE :-
Root Value :- Dorsal divisions of ventral rami of L2 L3 L4 spinal nerves.
Course :-
It enters the femoral triangle behind the inguinal ligament
Runs on the lateral side of femoral sheath
It ends by dividing in to anterior & posterior divisions, 2-3cm below the inguinal ligament by lateral circumflex femoral artery.
Branches in the Triangle :-
From the anterior division -
- 2 Cutaneous branches-
- Intermediate femoral cutaneous nerve- it supplies the skin over the front of thigh.
- Medial femoral cutaneous nerves- it crosses the front of femoral artery from lateral to medial side & supplies the skin over the upper part of medial side of thigh.
- 1 Muscular branch- to sartorius.
From the posterior division -
- 1 Cutaneous branch-
- Saphenous nerve- it descends along the lateral side of femoral artery in the triangle.
- 4 Muscular branches-
- Nerve to rectus femoris- it also gives a branch to hip joint.
- Nerve to vastus medialis- it also provides a branch to knee joint.
- Nerve to vastus lateralis- it also gives an articular twig to knee joint.
- Nerve to vastus intermedius- it also supplies articularis genu muscle & gives a branch to knee joint.
LATERAL FEMORAL CUTANEOUS NERVE :-
Root Value :- Dorsal divisions of ventral rami of L2 L3 spinal nerves.
Course :-
It enters the femoral triangle beneath the inguinal ligament, through a notch between anterior superior & inferior iliac spines
Runs over / through the sartorius muscle
It ends by dividing in to anterior & posterior divisions on the lateral side of the thigh
Branches in the Triangle :-
- Cutaneous branches- through anterior & posterior divisions it supplies the skin over the lateral aspect of thigh.
FEMORAL BRANCH OF GENITO-FEMORAL NERVE :-
- It is one of the terminal branches of genito-femoral nerve.
- Arises above the inguinal ligament.
Root Value :- Ventral rami of L1 L2 spinal nerves.
Course :-
It enters the femoral triangle beneath the inguinal ligament
Passes through the lateral compartment of femoral sheath, lying antero-lateral to the femoral artery
It ends after piercing the anterior wall of femoral sheath & fascia lata
Branches in the Triangle :-
- Cutaneous branches- to the skin over the upper part of front of thigh.
- Vascular branches- to femoral artery.
APPLIED ASPECTS :-
Femoral Hernia :-
- Herniation of abdominal contents (intestine) into the femoral triangle through femoral canal.
Direction of growth of hernial sac -
- Downwards- through the femoral ring into the femoral canal
- Forwards- through the saphenous opening
- Upwards- towards the inguinal ligament
Coverings of hernial sac -
- From within outwards-
- Peritoneal layer, femoral septum, anterior wall of femoral sheath, cribriform fascia, superficial fascia, skin.
Treatment -
- Manual reduction of hernial sac- by following the reverse order of direction of the sac.
- In strangulated femoral hernia- femoral ring is enlarged by incising the lacunar ligament.
Meralgia Paresthetica :-
- It is the loss of sensation over lateral part of front of thigh.
- Cause- compression of lateral femoral cutaneous nerve at anterior superior iliac spine, between the sartorius & inguinal ligament.
Femoral Artery :-
- Pulsations of the artery can be felt just below the inguinal ligament, by compressing it against the psoas tendon & superior ramus of pubis.
- Ligation of the artery proximal to the origin of profunda femoris, establishes collateral circulation through anastomosis between the branches of internal, external iliac arteries & profunda femoris artery.