Parotid Gland
PAROTID GLAND
- It is the largest of three paired salivary glands
- It is shaped like an inverted pyramid
COVERINGS
- The gland is invested by inner true & outer false capsules.
True Capsule :-
- It is formed by condensation of fibrous stroma
False Capsule
(Parotid Sheath) :-
- It is formed by the splitting of investing layer of deep cervical fascia.
- It has superficial & deep lamella.
Superficial lamella is strong.
- It is attached to zygomatic arch & blends with masseter muscle to form Parotido-masseteric fascia.
Deep lamella is thin.
- It is attached to the tympanic plate, styloid process.
- It is thickened between tip of styloid process and angle of mandible to form Stylomandibular ligament.
PRESENTING
PARTS
The gland presents -
- Apex
- Base
- 3 Surfaces – Superficial surface, Antero-medial surface, Postero-medial surface
- 3 Borders – Anterior border, Posterior border, Medial border
Apex :-
- It is directed below
- Overlaps the posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Structures passing through the apex-
- Cervical branch of facial nerve
- Anterior division of retro-mandibular vein
- Formation of external jugular
vein
Base :-
- It is concave and related to external acoustic meatus, temporo-mandibular joint
- Structures passing through the base-
- Temporal branch of facial nerve
- Superficial temporal vessels
- Auriculotemporal nerve
Superficial
Surface :-
It is covered by –
- Skin
- Superficial fascia
- Posterior fibres of platysma
- Superficial group of parotid lymph nodes
- Great auricular nerve
- Superficial lamella of parotid sheath
Antero-medial
Surface :-
- It is deeply grooved for the ramus of mandible
Relations-
- Masseter
- Ramus of mandible
- Capsule of temporo-mandibular joint
- Medial pterygoid muscle
Pierced by-
- Branches of facial nerve
- Maxillary artery
Postero-medial
Surface :-
Relations-
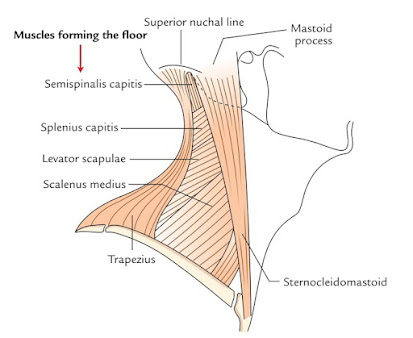
- Mastoid process with sternocleidomastoid & posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Styloid process & styloid groups of muscles
- Transverse process of atlas
- Internal carotid artery
- Internal jugular vein
- Last four cranial nerves
Pierced by-
- Facial nerve
- External carotid artery
Anterior Border
:-
- It separates superficial surface from antero-medial surface.
- Zygomatic branch of facial nerve
- Transverse facial vessels
- Upper buccal branch of facial nerve
- Accessory parotid gland
- Parotid duct
- Lower buccal branch of facial nerve
- Marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve
Posterior
Border :-
- It separates superficial surface from postero-medial surface.
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Posterior auricular branch of facial nerve
- Posterior auricular vessels
Medial Border
:-
- It separates antero-medial surface from postero-medial surface.
- It is also known as pharyngeal border as it comes in contact with the wall of pharynx.
PROCESSES
OF THE GLAND
Facial Process
:-
- It is a triangular projection superficial to masseter along the parotid duct.
Pterygoid
Process :-
- It is a triangular process from the deep part of gland.
- Situated between the mandibular ramus & medial pterygoid muscle.
Glenoid Process
:-
- It passes upward between external meatus & capsule of temporomandibular joint.
Pre-styloid
Process :-
- Part of the gland situated in front of the styloid process
- It is related to the internal carotid artery
Post-styloid
Process :-
- Part of the gland situated behind the styloid process
- It is related to the internal jugular vein
STRUCTURES
PASSING THROUGH THE
GLAND
From outside inwards –
- Facial nerve & its branches
- Retro-mandibular vein
- External carotid artery
Facial Nerve & Its Branches
:-
Facial nerve pierces the postero-medial surface of parotid gland
Within the gland it runs forward for 1 cm close to superficial surface
of the gland
Then it divides into Temporo-facial & Cervico-facial trunks
Temporo-facial Trunk-
- It turns upward within the gland.
- It subdivides into temporal & zygomatic branches.
Cervico-facial Trunk-
- It passes downward within the gland.
- It subdivides into buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical branches.
- The terminal 5 branches radiate like goose’s foot through anterior border of the gland.
- Such branching pattern is known as Pes anserinus.
Retro-mandibular
Vein :-
- It occupies the middle of the gland deep to facial nerve
- It is formed by the union of Superficial temporal & Maxillary veins.
- It divides into anterior & posterior divisions.
External
Carotid Artery :-
- It occupies the deep zone within the gland
- It ascends & divides into terminal branches- Superficial temporal & Maxillary arteries.
PAROTID DUCT (STENSEN’S
DUCT) :-
- It is 5 cm in length
- It is formed within the gland by union of 2 vertical ducts
Parotid duct emerges through anterior border of the gland
Passes forward on the masseter muscle between upper & lower buccal
nerves
It abruptly turns medially passes through the buccal pad of fat
Pierces the bucco-pharyngeal fascia & buccinator muscles
It passes obliquely forward between the buccinator & mucous membrane
of the cheek
Finally, the duct opens in to vestibule of mouth opposite upper second molar tooth
BLOOD SUPPLY
Arterial Supply
:-
- From branches of external carotid artery
Venous
Drainage :-
- Tributaries drain into external jugular vein
LYMPHATIC
DRAINAGE
Lymph drains into superficial & deep groups of parotid lymph nodes
Efferent vessels terminate into jugulo-digastric group of deep cervical
lymph nodes.
NERVE SUPPLY
Parasympathetic
Fibres :-
- Secreto-motor fibres cause watery secretion
Preganglionic fibres arise from inferior salivatory nucleus of medulla
Pass through the tympanic branch of glosso-pharyngeal nerve
Tympanic plexus
Lesser petrosal nerve
Relay into otic ganglion
Post ganglionic fibres pass through auriculo-temporal nerve to reach the
gland
Sympathetic Fibres
:-
- Secreto-motor fibres cause mucus-rich sticky secretion
- Vaso-motor fibres supply vessels of the gland
Postganglionic fibres derived from superior cervical sympathetic ganglion
Reach the gland through a plexus around the external carotid artery
APPLIED ANATOMY
Swelling of the Gland :-
- Painful due to the tight capsule
- Due to retrograde bacterial infection may leads to inflammation of the gland
- Viral infection of salivary glands
- Complications– inflammation of testes or pancreas.
Parotid Abscess
:-
- Pus can be drained by a horizontal incision (Hilton’s method)
Mixed Parotid Tumour :-
- Slow-growing, benign, painless tumour
Frey’s Syndrome
:-
- It’s a complication during the healing process of penetrating wound of parotid gland.
Penetrating wound of the gland damaging auriculo-temporal & great auricular
nerves
During healing process secreto-motor fibres of auriculo-temporal nerve
grow out & join the great auricular nerve
So that the fibres intended for salivary secretion reach the sweat
glands in the facial skin
When patient eats, beads of perspiration appear on the skin over parotid
gland.